In this article, you will find out about the advantages and disadvantages of sanitary landfills.
Deciding on the best way to handle rubbish, is a common challenge, especially in developing nations. Sanitary landfills offer one solution, but they come with pros and cons. This article will help you understand these landfill sites better, including their benefits and drawbacks.
Stay informed to make better choices.
Key Takeaways
- Sanitary landfills keep our cities clean by securely storing trash away from living areas, reducing the spread of diseases and supporting recycling.
- They can be sources of renewable energy through landfill gas extraction, turning waste management sites into power stations.
- Landfills release methane, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change and require constant maintenance to prevent environmental harm.
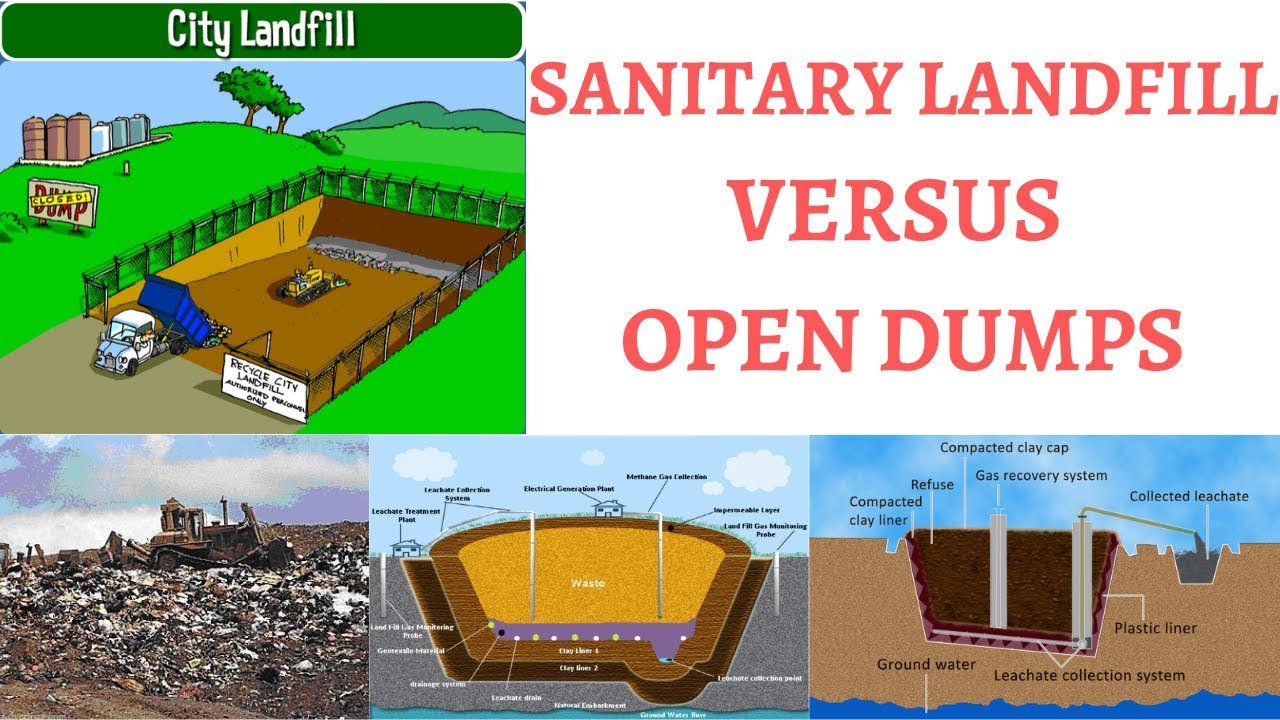
What are Sanitary Landfills?
We define them as the eco-friendlier cousins of traditional dump sites. The standards used for their design and construction vary around the world, but just 2 are the most commonly used, as follows:
- EU Landfill Directive compliant landfills
- US EPA compliant.
Picture this: instead of just piling garbage on the ground and calling it a day, sanitary landfills take a more organized approach. They carefully bury the waste in lined impermeable cells, and then they seal it off with a low-permeability capping to minimize environmental impact.
This method helps to control odours, keep pests at bay, and prevent pollutants from leaching into soil and water. It’s like giving the trash a proper send-off, ensuring it doesn’t harm our planet as it decomposes.
Understanding Sanitary Landfills
Sanitary landfills are carefully designed sites for disposing of waste. The site staff cover the trash with soil every night to keep it vermin free. These places also have systems to manage liquid waste, known as leachate, and gases that come from the rubbish breaking down.
Operating costs for sanitary landfills are quite low compared with any alternative trash disposal method, making them an economical choice for cities around the world. With advances in technology, these sites have become more efficient at keeping our environment cleaner.
These engineered facilities play a key role in modern waste management strategies by reducing pollution and controlling harmful emissions into the air and groundwater.
Landfill gas extraction is increasingly used as a profitable way to produce energy from the methane, showing how sanitary landfills can be more than just waste disposal sites.
Now let’s explore the advantages of using sanitary landfills for managing municipal solid waste.

Advantages of Sanitary Landfills
Sanitary landfills improve waste management. They provide environmental benefits and reduce hazardous spills, along with landfill gas extraction for power generation.

Improved Waste Management for Developing Nations
Landfills offer a cost-effective solution to manage large amounts of waste efficiently. They keep cities clean by providing a place where trash can be stored away from living areas.
This method helps control pests and reduces the spread of diseases. Through solid waste management practices, sanitary landfills ensure rubbish does not end up in open dumps, thus preventing environmental pollution.
These sites also support recycling efforts by segregating recyclable materials from the waste stream. By doing so, they promote resource recovery and contribute to a circular economy.
The operation of landfills minimises groundwater contamination through leachate management systems, protecting our earth’s precious water resources.
Environmental Benefits
Helping to keep air and water clean by containing harmful pollutants that can come from waste is the main function of any municipal landfill.
This means less air pollution and a healthier environment for everyone.
Sanitary landfills also promote land restoration wherever the site has been previously quarried. They do this by safely storing waste away from natural habitats, helping to protect ecosystems and wildlife. Keeping contaminants away from groundwater ensures that our quality of water stays high, making life better not just for us, but for all living creatures.
Reduced Hazardous Spills
Sanitary landfills have normally have a solid system in place to cut down on hazardous spills. They use engineered barriers that are designed to keep dangerous wastes from leaking out. This setup protects our environment and public health by preventing contamination of groundwater and soil.
Proper hazardous waste management ensures these harmful substances stay locked away for many years, reducing risks to air quality and human activities around landfill sites.
These measures also help in pollution control. By stopping hazardous waste from spilling, sanitary landfills play a crucial role in maintaining clean and healthy living conditions for communities nearby.
These landfills are crucial for protecting the planet and its inhabitants from potential harm from industrial waste and other toxic materials because the focus on prevention means fewer opportunities for disease-causing agents to spread.
Landfill Gas Extraction and Power Generation
Moving from reducing hazardous spills, we also see how landfills can become sources of renewable energy. Landfills generate gas as waste breaks down over time. This gas is mostly methane, which can be dangerous if released into the atmosphere but is valuable when captured and used as an energy source.
Workers install systems to collect this gas directly from the landfill site.
These collected gases then power generators or get processed into biofuel. Producing energy in this way helps cut-down on greenhouse gas emissions by using methane that would otherwise contribute to climate change.
It turns waste management sites into power stations, contributing to local economies and creating jobs in environmental engineering and energy production sectors. This process underscores landfills’ role in a circular economy where waste materials are reused for their energising potential.
Disadvantages of Sanitary Landfills
Sanitary landfills release methane, contributing to climate change. Nutrients in waste are wasted and landfill maintenance poses cost challenges. Methane gas extraction is necessary to mitigate environmental impacts.
Groundwater pollution can occur due to the disposal of hazardous substances in landfills. Additionally, it takes a long time for waste to become inactive within sanitary landfills.
Methane Emissions and Climate Change
Methane gas, a major component of landfill emissions, plays a significant role in climate change. Landfills are responsible for 12% of global methane emissions. This potent greenhouse gas traps heat in the atmosphere far more effectively than carbon dioxide, accelerating global warming.
Methane capture technologies offer some hope by converting this harmful emission into a renewable energy source, but face challenges in widespread implementation.
Emissions from sanitary landfills not only affect the climate but also pose risks to health and safety due to the release of volatile organic compounds and other hazardous substances.
The next topic explores waste’s impact on nutrients and soil health.
Waste of Nutrients
Landfill sites become breeding grounds for bacteria and contaminants. These unwanted guests lead to the loss of valuable nutrients in the soil. Plants and local ecosystems suffer as a result.
The ground becomes less fertile, impacting food chains and biodiversity.
Hazardous chemicals not disposed of properly add to this problem. They contaminate the soil, robbing it further of nutrients vital for plant growth. This contamination poses risks to animal life too, disrupting habitats and endangering species that rely on these environments for survival.
Cost and Maintenance Challenges
Moving from the loss of valuable nutrients in waste, we encounter significant cost and maintenance challenges with sanitary landfills. Running these sites is expensive due to the need for advanced technology and intensive labour.
New methods and new laws for managing waste add to upfront costs. They also bring ongoing expenses for keeping operations smooth.
Managing a landfill requires constant attention to environmental protection. Efforts include controlling smells, preventing runoff, and dealing with pests. The production of leachate and gases demands investment in systems like geosynthetic clay liners and gas extraction facilities.
These measures aim at reducing health risks and environmental damage but push up maintenance costs considerably.
Environmental Impact
Amid the cost and maintenance challenges, it’s crucial to recognise the severe environmental impact of sanitary landfill sites. These sites contribute significantly to pollution, posing threats to land, sea, and air.
The clearing of forested areas for landfill sites not only disrupts natural habitats but also deprives the Earth of carbon absorption. Furthermore, irresponsible disposal of hazardous chemicals can contaminate soil, groundwater, and air, endangering entire ecosystems.
The proliferation of bacteria at landfill sites disrupts delicate ecological balance and poses risks to local flora and fauna. Soil pollution, deforestation, hazardous waste disposal issues are some examples that highlight how these sites have far-reaching effects on the environment as a whole.
Time to Inactive Storage
Sanitary landfills reach the inactive storage phase when they can no longer accept waste due to reaching capacity. At this point, post-closure care begins with regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure that the landfill is not causing harm to the environment or public health.
The closure process involves covering the landfill site with a protective barrier, such as soil and vegetation, which helps minimise water infiltration and controls potential emissions.
Inactive storage in sanitary landfills is an essential phase that requires ongoing attention despite ceasing waste acceptance. Regular checks are necessary for maintaining environmental safety and preventing any adverse impacts on nearby communities.
Conclusion
Sanitary landfills offer effective waste disposal and environmental protection but carry drawbacks such as methane emissions, nutrient wastage, cost challenges, and environmental impact.
They play a crucial role in waste management by capturing methane gas and complying with regulations. Despite their advantages, they can lead to pollution, climate change issues due to methane emissions, and the need for careful monitoring of hazardous chemicals.
Understanding these benefits and drawbacks is essential for implementing sustainable waste management practices.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of sanitary landfill sites?
Sanitary landfill sites help reduce waste by burying trash in engineered landfills. They also control pests and odours, making them better for the environment than open dumping.
2. How do sanitary landfills impact the environment?
While they aim to manage waste better, sanitary landfills can still harm the environment. They might lead to soil contamination, affect air quality with particulate matter, and cause pollution.
3. Can sanitary landfills produce bad smells and noise?
Yes, even though these sites try to control odours and use pest control methods, trucks coming in and out can create noise while food waste decomposes creating unpleasant smells.
4. Are there any health concerns linked to living near a landfill site?
Living close to landfill sites may expose people to harmful substances like dioxins which come from the incineration of waste or litter that flies away, contaminating surrounding areas, which could endanger health.
5. Why do some people oppose new landfill sites?
People often worry about pollution, and health risks from contaminants like dioxins or particulate matter affecting their well-being or privacy due to increased traffic from trucks transporting construction debris or yard waste.
6. Do environmental agencies support the use of sanitary landfills?
Environmental agencies see engineered landfills as a necessary solution for managing society’s waste reduction goals but stress on implementing strict regulations against fly-tipping and ensuring proper excavation practices are followed.
Landfill Sites – 3 Compelling Reasons to Bury the Use of Dumps
Landfill Sites are not sustainable, and here are 3 compelling reasons to bury the idea that we continue to use landfills (dumps) for municipal waste beyond the next 10 years. All waste has to be disposed of in a safe manner. If not it is a major health problem in densely populated urban areas, second […]
What is a Landfill Liner? Geomembrane Linings Explained
Landfill linings are physical barrier systems intended to, as far as possible, prevent the escape of water and gases out of the body of the landfilled waste. A Landfill Liner is placed at the bottom and sides of modern landfills and are continuously welded to as far as possible provide a watertight seal. They are […]
All UK Landfills to Close within 5 Years? Zero Waste UK
In this article we make the prediction that all UK Landfills will close within 5 Years. The current trend in waste reduction/ diversion from landfill shows that the nation will achieve Zero Waste to Landfill and quite soon as well. That momentous occasion will take place in 5 to 6 years time, according to the figures […]
The History of Landfill Lining Design [Infographic]
The Evolution of Landfill Lining Design in the UK from Dilute and Disperse to Full Containment The image above is one that we published back in 2004 and is one of the most important progressions in the history of landfills in the UK. It was a webpage in itself and rendered in efficient HTML code […]











